
 Otorhinolaryngology (ENT)
Otorhinolaryngology (ENT)Otorhinolaryngology specialises in the treatment of diseases related to the ear, nose, throat and head and neck. The ear, nose and throat are three interconnected organs in the skull. Lesions in each of these regions can affect each other. Specialists Central provides consultation, risk assessment, examination, diagnosis, surgery and treatment for patients with ENT diseases in Central, Hong Kong Island and Mong Kok, Kowloon. For enquiry about specialist fees and appointments, please contact us.



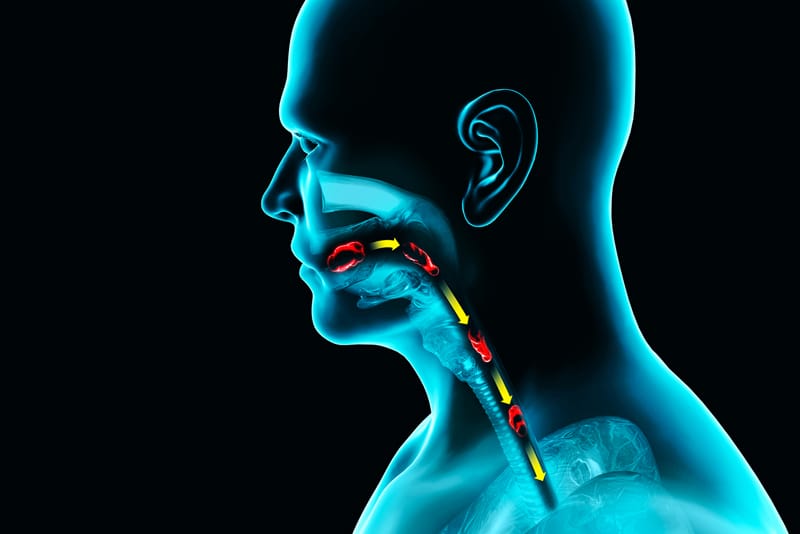

Could you be suffering from swallowing difficulties?
Fill out self-test survey
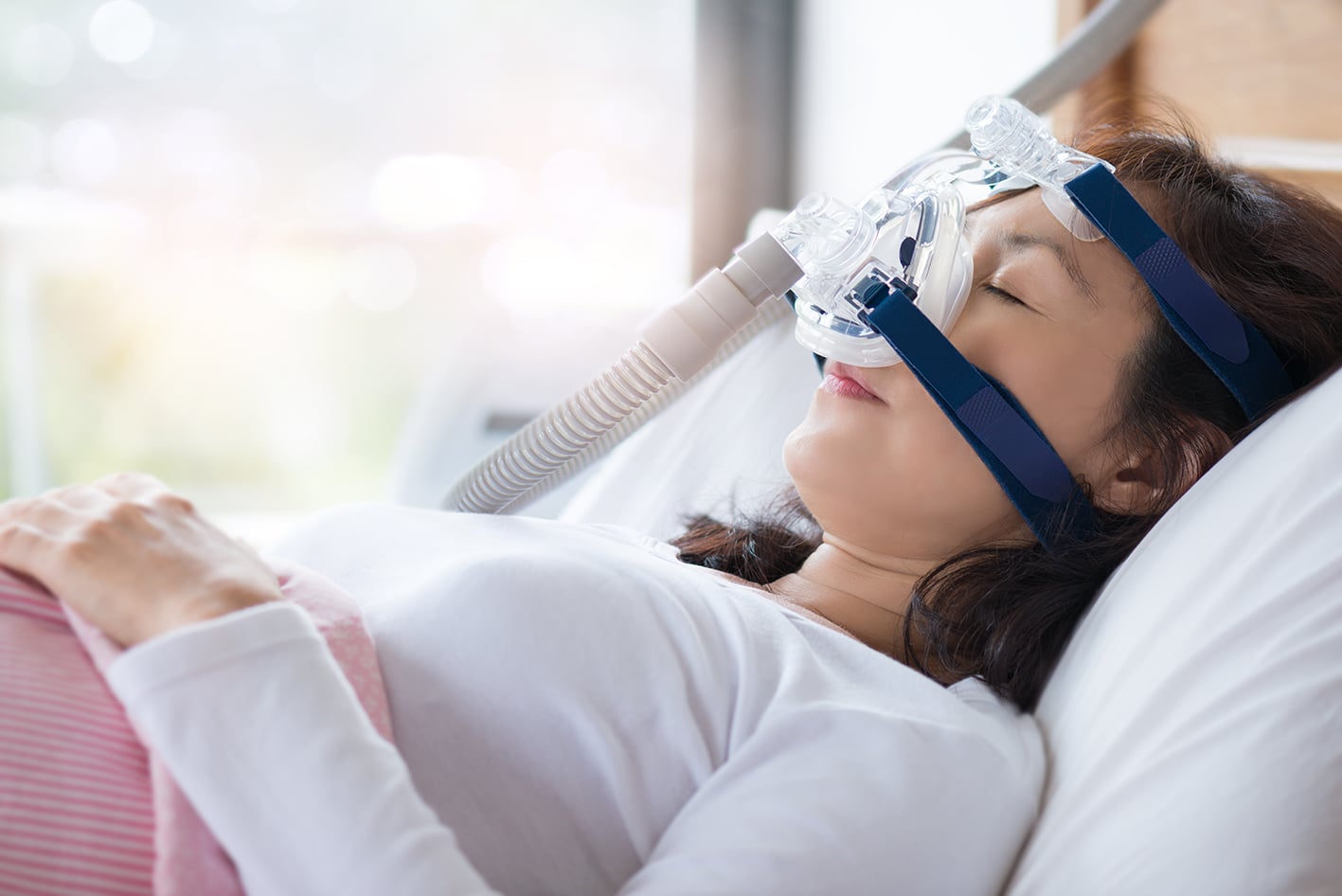
It is becoming increasingly common in Hong Kong, with over 100,000 people currently suffering from the disorder. Patients will stop breathing intermittently during sleep for a few seconds to a minute or more at a time, which can happen a dozen or even hundreds of times a night. The oxygen level in the patient’s blood drops during asphyxia, making it difficult to sleep tight and get enough sleep due to frequent awakenings.
Potential Risks
Symptoms of Sleep Apnoea
Could you be suffering from sleep apnoea?
Fill out self-test survey
Our clinic provides one-stop ENT consultation, examination and treatment services to meet the needs of patients holistically, from preventive screening, medication to surgical treatment. The scope of services includes:
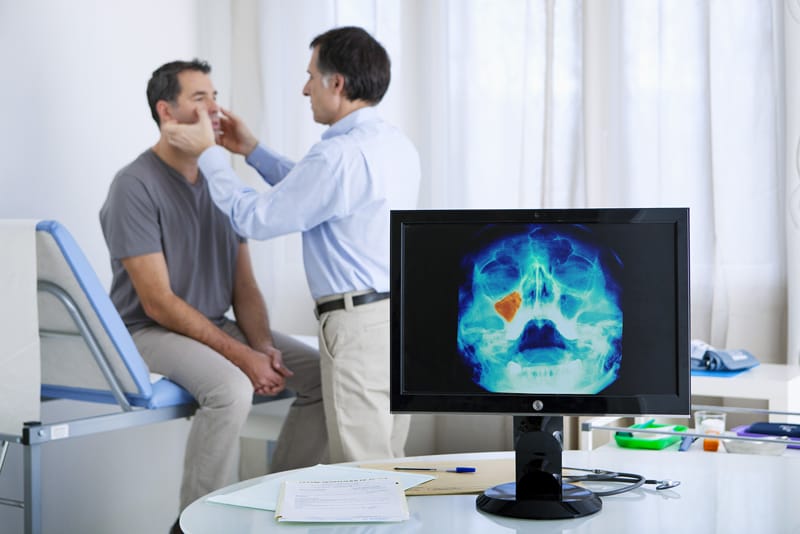
Screening Programme for Nasopharyngeal Cancer: Nasopharyngeal cancer is one of the commonest cancers in Hong Kong, where there are about 900 new cases each year, with the incidence rate for men three times higher than that for women. The nasopharynx is located in quite a hidden area and there may be no obvious symptoms in the early stages of the cancer, so it is not easy to detect. The screening programme provides early detection of nasopharyngeal cancer for high-risk individuals before they develop any symptoms so that early and proper intervention could be given.
The services of the programme include ENT specialist consultation, nasopharyngoscopy, EBV serology test.
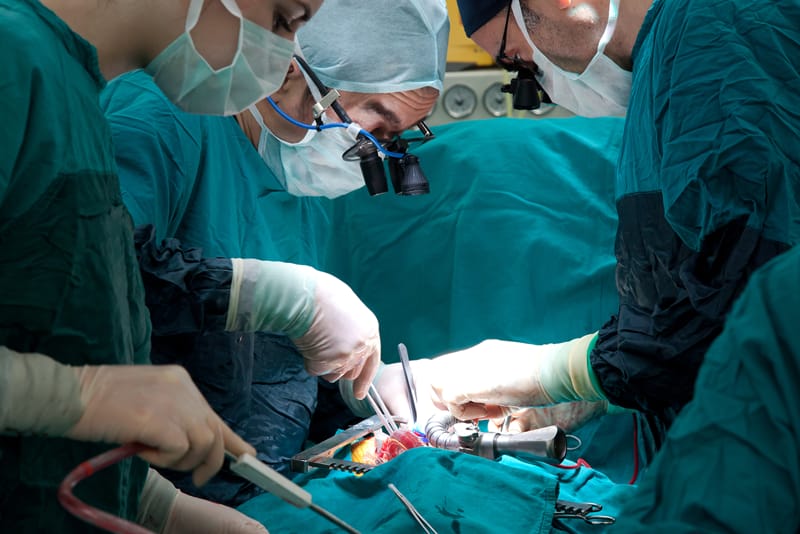
Otology (Ear): cochlear implant, myringotomy and ventilation tube insertion, tympanoplasty, myringoplasty & tympanoplasty, surgeries related to various ear diseases, bone anchored hearing aid implant, Stapedectomy and ossiculoplasty, endoscopy, otitis media treatment, hearing assessment and related services.

Cochlear Implant Surgery: The cochlear implant is an implantable hearing aid designed for people with severe hearing impairment. When fitted behind the ear via minimally invasive surgery, the device will process the incoming sounds and send signals to the auditory nerves, enabling people with hearing impairment to produce a hearing sensation. The patient will need a detailed medical assessment to determine if the surgery is appropriate.

Rhinology (Nose): Allergic rhinitis test, nasopharyngoscopy, diagnosis of early-stage nasopharyngeal carcinoma, a comprehensive range of nasal surgery, minimally invasive endoscopic sinus surgery
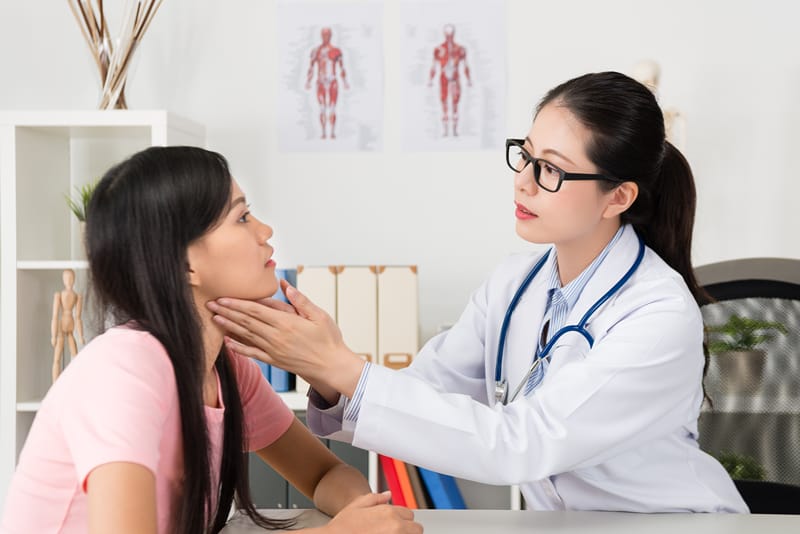
Laryngology (Throat): treatment of thyroid and salivary gland disorders, paediatric respiratory surgery, treatment for vocal cord paralysis, examination of vocal cord for diagnosis and treatment of laryngeal carcinoma, speech-language and voice diagnosis and treatment
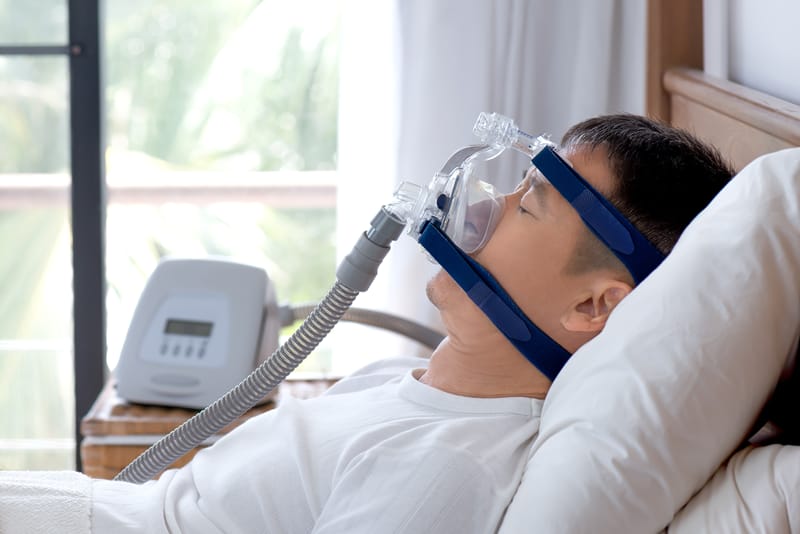
Sleep Apnoea Treatment: continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) machine, mandibular advancement device, radiofrequency ablation, uvulopalatopharyngoplasty (UPPP), Robotic Surgery
The above is not intended to be an exhaustive list of examinations and treatments offered by our clinic. Please seek professional advice from an ENT specialist before undergoing any treatment. Where appropriate, Specialist Central will provide referrals for patients requiring ENT surgery carried out by our specialists.

Specialists Central’s medical team consists of specialists in otorhinolaryngology, audiologists, speech therapists and experienced healthcare professionals, offering specialist services for the treatment of diseases of the ear, nose, throat, head and neck. We have an array of advanced and precise medical facilities in place to cater for various ENT applications. We are committed to providing accurate diagnoses and developing a personalised care plan for every patient.
1. Is snoring equivalent to sleep apnoea?
Loud snoring is one of the symptoms of sleep apnoea. It is, however, not the same as having sleep apnoea. The muscles of the throat and nasal passages relax when you are sound asleep, and the relaxed muscles may cause the airways to collapse and narrow. Snoring occurs when air passes through the narrow airway during inhalation, causing the soft tissues around the throat to vibrate. Apart from sleep apnoea, snoring can also be caused by nasal congestion, alcohol consumption, laryngitis and enlarged tonsils, etc. If in doubt, it is advisable to seek medical help. After a sleep test or analysis, you will be assessed and diagnosed by an ENT specialist and be prescribed the appropriate treatment.
2. When do I need to have my tonsils removed?
The tonsils are one of the lymphatic tissues in the mouth. In general, tonsillitis is usually treated with prescription medication and will be cured within a short period. However, in patients with frequent or severe tonsillitis, tonsillectomy may be recommended to solve the issue.
3. Is choking on drinks the same as dysphagia (swallowing problems)?
Choking easily, being one of the symptoms of dysphagia, does not mean the same as the problem. People normally do not have difficulty swallowing, but they may be choked by water or food, for an instant, if they eat too quickly. Swallowing problems can be caused by aging or disease. When the swallowing muscles are weak and the sensory function is poor, the patient is prone to choking when eating or drinking. In severe cases, choking can be fatal due to food blocking the airway or choking into the lungs. Patients are advised to receive proper treatment as soon as possible.
4. Do I need a referral from a general practitioner to make an appointment for ENT?
Specialist consultation at Specialists Central does not require a referral from a general practitioner. You can call our clinic directly and make an appointment with our ENT specialists.
5. Can I have an ENT consultation and treatment on the same day?
An appointment is required for our specialist services. You are advised to contact us to make an appointment. We will schedule medical consultation for a doctor to understand your condition before arranging appropriate exams and treatment.
6. What are the medical fees? Do specialist clinics accept health care vouchers? Can I pay via medical insurance?
Medical fees are determined based on the severity of the patient’s condition, his/her health status, the complexity of the treatment or surgery received, and the postoperative care services.
Health care vouchers can cover some of the costs. Please feel free to contact us for further information.
The medical policy and coverage of each patient vary. Please check with your insurer for the claims process, costs and other details before receiving our specialist outpatient services.